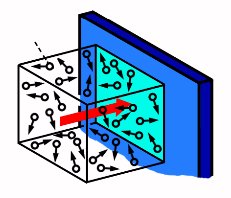
Implementation
An example for "A" type class
Basics of thermodynamics
Kinetic gas model
The molecules can interact with each other and the wall.
The pressure of the gas comes from the interaction of the wall with the molecule.


Pressure on the surface. Pressure of N particles
![]()
The temperature of the gas is determined by the average kinetic energy of the particles.
![]()
Diffusion of
two different types of gas.
Gases of different particles penetrate through each other, and get mixed.
Equipartition theorem:
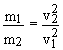 |
Gas Laws
Boyle-Mariotte
Izothermic process (T -const.)
Gay-Lussac I.
Izobar process (p -const.)
Gay-Lussac II.
Izochor process (V -const.)
Unified Gas Law
pV=nRT
Gases in
gravitational field
(atmosphere of the earth)
The particles
move but also gravity affects them.
The density on the surface is higher than at the top of the hills or higher above.
Brownian motion
Experiment:
Observation of
dust particles from the direction of light coming from a slide projector.
Permanent unregular movement, zigzagged trace.
Cause: the large observable particle gets unregular pushes from the particles of the gas or fluid.
Application
Heat engine
Carnot cycle
Cooling machine
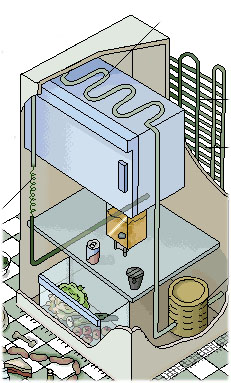
Diesel engine